PUBLIC FINANCES
The purpose of this section is to provide an overview of the finances of the public sector.
Public Sector
The public sector consists of a public administration and public corporations. The public administration includes authorities and institutions which mainly offer non-market services, redistribute income and wealth, and generally seek to promote economic development.
Non-market services are services actively controlled by public authorities and available free of charge for individuals and businesses. Public services are financed mainly through taxes. Some public services such as childcare are partly funded through user fees which, however, cover less than half the costs.
Public administration and service in Greenland include three sub-sectors: the municipal sector, the self-governed sector and the state. In this regard, a distinction is made between the state sector in Greenland and the Danish government.
The state sector in Greenland includes economic activity in areas still managed and funded directly by the Danish government. According to existing international guidelines, only expenses incurred in or near Greenland are included.
A special feature is the large public involvement in business. According to international guidelines, the companies are divided into 1) companies which are part of government, 2) public corporation-like units (so-called quasi-companies) and 3) public companies.
A company is considered part of the administration if a substantial part but less than 50 per cent of the operating costs are covered by the sales of goods and services. The operating expenses of the company are included as part of the public consumption and divided into compensation of employees and consumption in the production while revenues are included as sales of goods and services. Examples of such companies are Kanukoka, Asiaq / Misissueqqaarnerit (Greenland Survey) and Kalaallit Nunaata Radioa (KNR).
The public part of the corporate sector consists of publicly controlled and / or owned companies which operate on market terms. A distinction is made between:
- Public company-like businesses (so-called quasi-companies) and
- Public companies
Public corporation-like units are entities organized under the Government of Greenland or the municipalities, where more than 50 per cent of the current operating costs are covered by sales of goods and services on market terms. They often referred to as quasi-companies. In the self-governed sector Nukissiorfiit (The Power Supply of Greenland) and Mittarfeqarfiit (Greenland Airport Authority) are considered public quasi-companies.
Public companies are owned and / or controlled by the government, e.g. through a majority holding. These companies are usually organized as private legal entities (typically limited liability companies). Examples of public companies are Royal Greenland Ltd, KNI Pilersuisoq Ltd, and Tele Greenland Ltd.
Figure 1
The Public Sector by Area of Administration
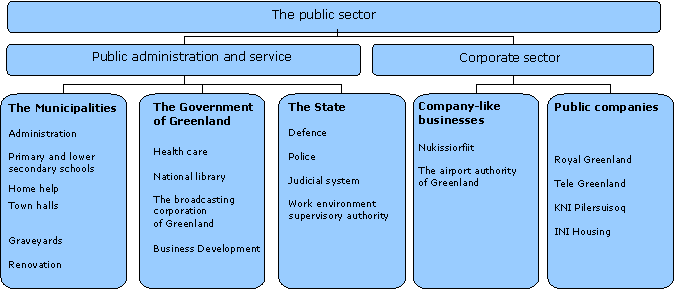
Source: Statistics Greenland
The public sector has in recent years undergone major changes in connection with the municipal reform reducing the existing 18 municipalities to four in 2009.
Public Expenses
The composition of public expenditure can be illustrated in different ways.
A real economic breakdown of expenditure shows that the public consumption has constituted a growing proportion of the total expenses since 1986. The government consumption consists mostly of salaries to employees and purchases of goods in connection with the production taking place.
In 2009, government consumption amounted to 73 per cent of the public expenditure. The current transfers, mainly pensions, unemployment benefits and the like, amounted to around 21 per cent of the total that year.
Capital expenses, covering among other things investments in schools, hospitals, and roads amounted to about 6 per cent of the total in 2009.
Figure 2
Operating and Capital Expenses in Public Administration and Service
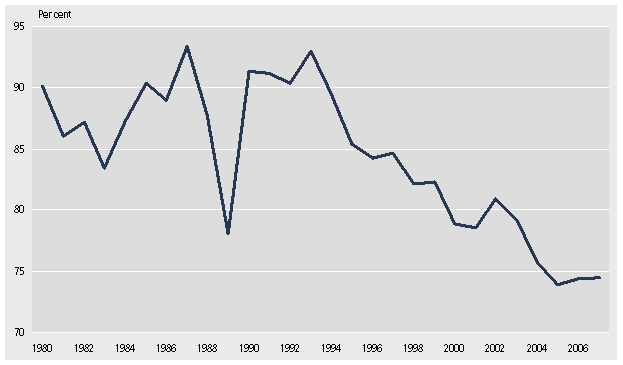
Source: Statistics Greenland
Figure 3
Public Expenditure by Real Economic Categories
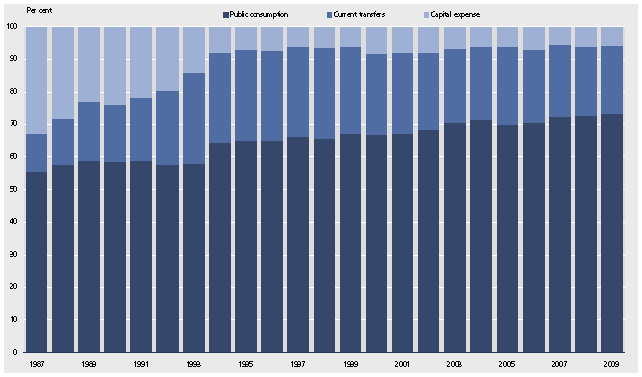
Source: Statistics Greenland
The functional distribution shows government expenditure by purpose. In 2009, 59 per cent of the costs were connected with three major areas, education, health care, and social welfare. These areas are often considered core services in a modern welfare state.
A breakdown of other operating and capital expenses is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4
Functional Distribution of Operating and Capital Expenses in 2009
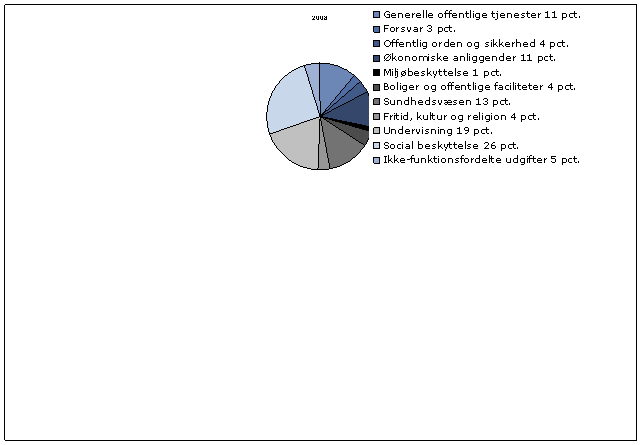
Source: Statistics Greenland